Due to easy maintenance and cleaning, compact designs and heat exchange efficiency, stainless steel plate heat exchangers are widely used in sanitary applications such as food, beverage, pharmaceuticals, etc.
In the production process of orange juice, stainless steel plate heat exchangers are required before and after pasteurization (heating to 85-95°C), preheating and cooling, enzymatic hydrolysis or concentration. In these processes, sugars, pectin, organic acids (such as citric acid, malic acid) and calcium and magnesium ions in orange juice may cause different forms of scaling and deposition, affecting the heat transfer efficiency of the equipment, contaminating the product, increasing energy consumption and even causing equipment shutdown.
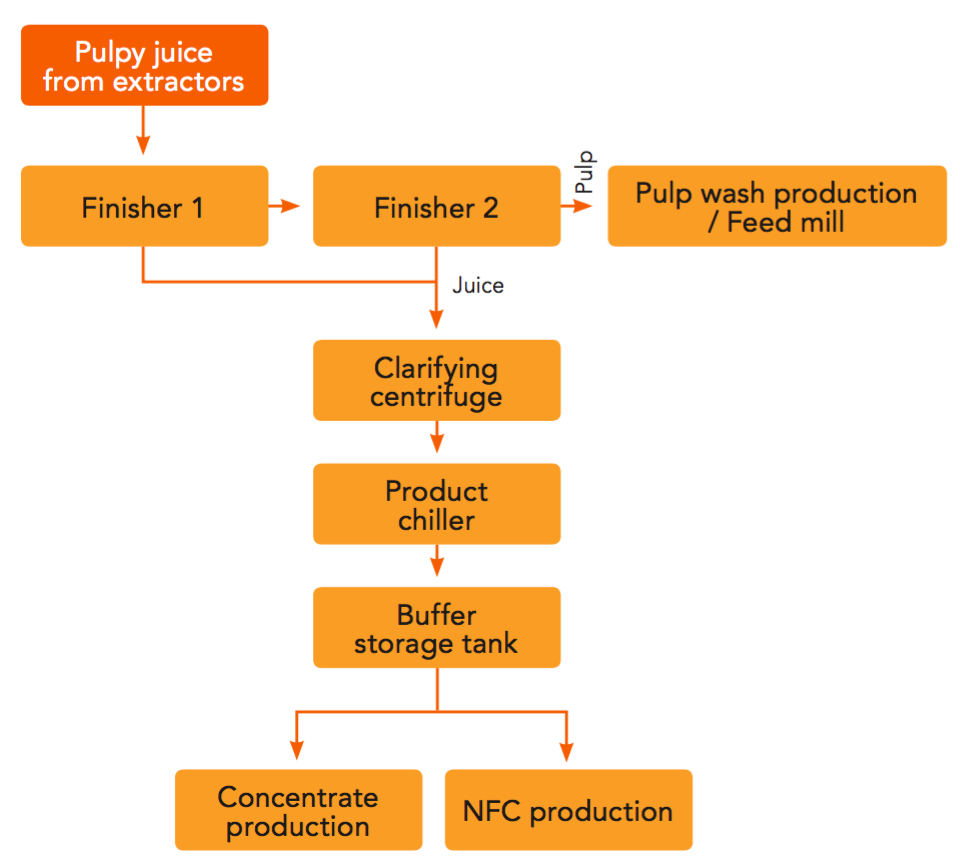
Fruit Processing
a. Coarse filtration: Install a 200-400μm filter before entering the stainless steel heat exchanger to remove peels, seeds and pomace to prevent clogging and deposition.
b. Degassing (optional): This is Applicable to high-oxygen juice to reduce oxidative deposition.
c. Pectinase treatment: Ensure that pectin is fully degraded during the enzymatic hydrolysis process to reduce the risk of deposition.
d. Control the quality of raw water: If water is used (such as dilution or CIP), ensure that its hardness is <50 mg/L (in terms of CaCO₃).
a. Material selection: PHE plate use 316L stainless steel (more resistant to citric acid corrosion), heat exchanger gasket use Food-grade EPDM or HNBR rubber strip, heat-resistant and acid-resistant
b. Plate structure: Choose a high-turbulation corrugated type to form strong turbulence, improve the self-cleaning effect, and avoid corner deposition.
c. Heat exchange section design: The heating and cooling sections are divided into zones to facilitate CIP cleaning according to functional sections.
a. Flow rate control: The orange juice flow rate should not be too low, and it is recommended to be ≥1.0 m/s to prevent deposition. Prevent local stagnation areas (such as the edge of the heat exchange plate and dead corners).
b. Temperature control: The heating zone should not heat up too fast, and ΔT should be controlled within a reasonable range (20-40°C). Avoid the plate surface exceed 100°C (sugar is easy to caramelize).
c. Stable operation: Reduce start-stop and operation fluctuations to avoid deposition caused by temperature difference shock.
Recommended implementation of CIP cleaning after each production batch or at the end of each day.
a. Monthly random inspection of the plate for scale or pitting.
b. Manual disassembly and cleaning every quarter to check for dead corner deposition.
c. Replace or flip the sealing gasket every six months to ensure sealing.
d. Check whether the flow and pressure difference are abnormal (scaling will cause increased pressure difference).
| Parameter | Recommended Value |
| Material | 316L stainless steel plate + EPDM gasket |
| Plate Gap | 3~5 mm |
| Orange juice in and out temperature | 20℃ → 90℃ |
| Water Temperature | 95℃ |
| Flow Rate | ≥1.0 m/s |
|
Measuring Differential Pressure |
< 0.5 bar |
__________
As a professional heat exchange equipment manufacturer, we specialize in stainless steel plate heat exchangers with high sanitation standards for the food and juice industries. Committed to improving heat exchange efficiency, reducing maintenance costs, and extending equipment life. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your business!
