In a glycol plate heat exchanger, two fluids (a mixture of glycol and water on one side and water, air, etc. on the other) transfer heat between metal plates. Heat exchangers usually comprise a series of stainless steel or other metal plates with strong thermal conductivity. Due to the good thermal conductivity of the metal plates, there are flow channels on the surface of each layer of plates, allowing the fluid to flow between the plates, and the heat will flow from the higher temperature side to the lower temperature side to complete the heat exchange. To improve the heat transfer efficiency, the heat exchanger plate has a corrugated structure design, which can increase the turbulence of the fluid and enhance the heat transfer effect.
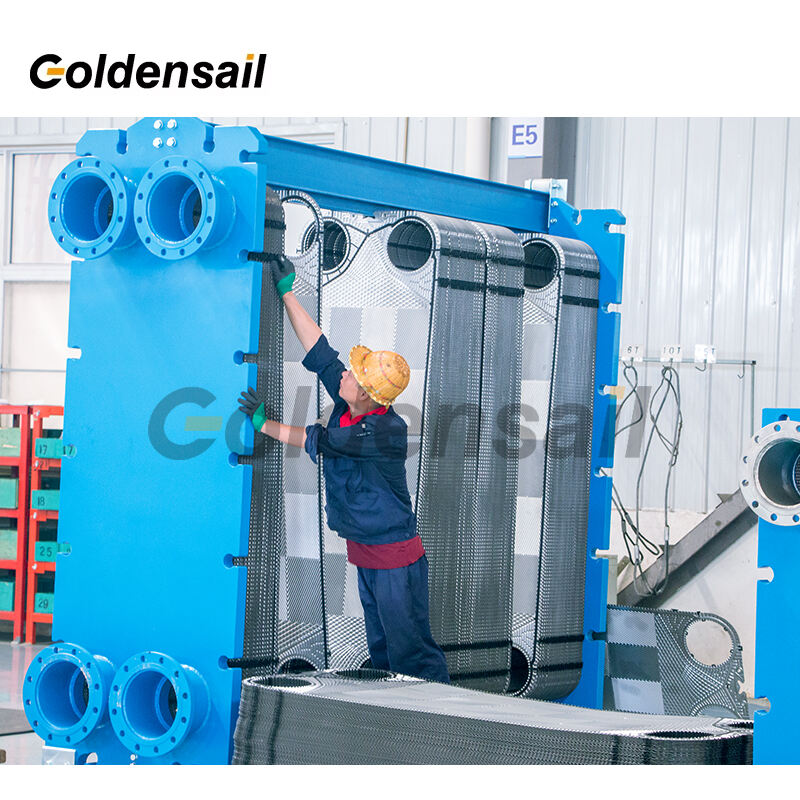

Freeze Protection: Glycol mixtures prevent freezing in cold environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Compatible materials ensure long-term durability.
Energy Efficiency: High heat transfer efficiency reduces energy consumption.
Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of temperatures and applications.